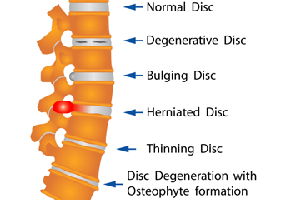
What is Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)?
Lumbar degenerative disc disease (DDD) is defined simply as the wear and tear of the intervertebral disc, which may result from normal aging or be due to longstanding trauma. It involves small tears in the annulus of the disc (elastic outer ring of collagen fibers) and lack of water content of the nucleus of the disc (soft gel center). The degenerative cascade can lead to disc bulging, development of bone spurs (or osteophytes), and loss of disc space height and/or alignment, which can cause nerve impingement. DDD can also lead to degenerative instability, the loss of the ability of the spine under physiologic loads to maintain its pattern of normal movement due to disc degeneration.
Common Symptoms of Degenerative Disc Disease:
• Pain at the site of the injury
• Pain, numbness, or tingling in the legs
• Strong pain that tends to come and go
• Pain is worse when bending, twisting, and/or sitting
• Lying down relieves pressure on the spine
Diagnosing Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease:
Your doctor will perform a physical examination to identify areas of pain and weakness and will evaluate your balance and the overall movement of your spine. Your doctor will also collect information about the history of your symptoms, including medicine you have taken for your condition. After your examination, your doctor may use tests to help establish his or her diagnosis. Some of these tests include x-ray, CT (computed tomography) scan, and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). Together, all of these techniques help to confirm a diagnosis of lumbar DDD.
Treatment options:
The following provides an overview of standard non-surgical and surgical treatments for lumbar degenerative disc disease.
Non-surgical treatment:
If lumbar degenerative disc disease is established as a diagnosis, your doctor will likely recommend one or more of the following treatments:
• Physical therapy and strengthening exercises
• Rest and a restriction of physical activity
• Injections (corticosteroids) to help reduce the pain and swelling
• Medications and analgesics to reduce pain and swelling; typical medications include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Your doctor can discuss recommended treatment options based on your individual needs.
Surgical treatment:
Below are some of the surgical procedures used to treat degenerative disc disease.
• Maximum Access Surgery Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (MAS PLIF):
Posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) is a surgical technique that attempts to eliminate instability in the back and pain in the lower back and lower extremities. A MAS PLIF achieves this by using a less disruptive approach to decompress nerve roots and fuse one or more vertebrae together to reduce motion. Learn more about the MAS PLIF procedure here.
• Maximum Access Surgery Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (MAS TLIF):
The MAS TLIF procedure is a technique that attempts to eliminate instability in your back through a less invasive approach to fuse one or more vertebrae together to reduce their motion. Learn more about the MAS TLIF procedure here.
• eXtreme Lateral Interbody Fusion (XLIF®)
The XLIF procedure is a minimally disruptive surgical procedure performed through the side of the body. It is designed to treat a range of spinal conditions. Using patented nerve monitoring technology, the surgeon gains lateral (side) access to the spinal spine, helping to avoid any major nerves in the area between the incision and the column. The XLIF procedure does not require an anterior (front) or posterior (back) exposure, and therefore does not present the same risks of vascular and/or neural injury as traditional approaches. Learn more about the XLIF procedure here.
I have more questions, who can I ask?
In addition to consulting with your physician and medical teams, it often helps to speak to someone who has had a similar condition. To connect with a Patient Ambassador dealing with degenerative disc disease, please complete our request form.